The causes of diffuse hair loss can be numerous. In order to determine these, a detailed examination by your doctor is advisable. Nevertheless, diffuse hair loss itself is not classified as a specific clinical picture, but rather as a symptom of an existing health problem. Below you will find an overview of the most common causes of diffuse hair loss:
Side Effects of Medication
There are numerous medications that can trigger diffuse hair loss as a side effect. The probability of this is low, but possible. Hair loss usually occurs two to four months after taking the medication. These medications include:
- Antihypertensive, anticoagulant and antihypertensive drugs
- Retinoids
- Various antibiotics
- Psychotropic drugs
- Epilepsy drugs
- Hormone-containing drugs
- Anti-inflammatory painkillers
- Chemotherapeutic drugs
If your doctor can attribute the diffuse hair loss to a medication, it is highly unlikely that the hair loss will be permanent. This does not apply to chemotherapy drugs, which can permanently damage the hair follicles. If you are taking a medication that can be replaced, this may be an option. However, this is only possible if you are not dependent on a specific active ingredient. Please also note that you should not stop taking your medication on your own.
Hormonal Changes
As hormones influence hair growth and hormonal fluctuations are part of the nature of the female body, women are particularly susceptible to diffuse hair loss. The hormone that plays a decisive role here is the sex hormone oestrogen.
Hair loss can occur at different stages of life, such as during puberty, after childbirth, during breastfeeding, when taking or stopping the contraceptive pill, when using a hormone coil or during the menopause due to changes in hormone levels. However, as hormone levels regulate themselves in most cases, there is no cause for concern. Once the hormones are back in balance, hair density should also return. However, the situation is different with hair loss due to the menopause: In this case, a thinning head of hair can remain permanently due to the drop in oestrogen levels. After medical clarification, treatment with minoxidil can be considered.
Thyroid Disease
Another factor that can influence the human hormone balance is an overactive or underactive thyroid gland or an autoimmune thyroid disease such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Diffuse hair loss can also occur as a symptom here. However, if the thyroid disease is treated appropriately, the diffuse hair loss in this case is only temporary. Hair growth normalizes itself after a while. Thyroid disorders are often accompanied by a nutrient deficiency. A corresponding blood test by a doctor not only provides information about the function of the thyroid gland but also about the nutrient status.
Nutrient Deficiency
Hair requires a sufficient supply of proteins, vitamins, trace elements and other essential substances. Iron, zinc, selenium, amino acids, vitamin A and omega-3 fatty acids, Biotin, in particular, are important for healthy hair and influence growth. Therefore, make sure you eat a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables, nuts, olive oil and preferably plant-based protein. Vegetarians, vegans, athletes, people with gastrointestinal diseases and pregnant women in particular should pay attention to their nutrient intake. If there is a nutrient deficiency, the hair roots are no longer sufficiently supplied with nutrients. Hair may fall out as a result. If necessary and after consulting a doctor, a diagnosed nutrient deficiency can easily be treated with additional nutritional supplements.
Genetics
Genetics cannot be held directly responsible for diffuse hair loss, as genetic hair loss is a disease in itself. However, diffuse hair loss and hereditary hair loss can occur at the same time.
Stress
To date, there have not been enough studies to scientifically prove the connection between stress and hair loss. Nevertheless, sufficient studies indicate that stress can have a negative effect on both the body and the mind. It is assumed that stress releases more pro-inflammatory substances that can promote hair loss.
Poisonings
Heavy metals such as mercury, cadmium and thallium can cause diffuse hair loss. However, other physical symptoms occur more frequently than just hair loss.
Incorrect Hair Care
Chemical coloring can put a lot of strain on the hair, but does not directly lead to diffuse hair loss. Dyeing destroys the natural cuticle and care products can no longer be properly absorbed. Blood circulation to the scalp is also impaired, which means that the hair roots can no longer be properly supplied with nutrients. When buying care products, you should also look for a mild formula without chemical additives, as these can damage the hair.

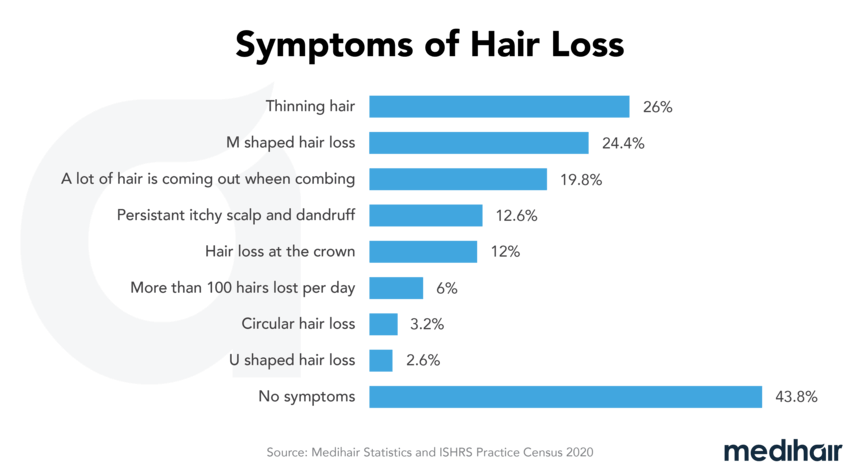
Both men and women can be affected by diffuse hair loss. With this type of hair loss, the scalp shines through and the hair is no longer as full and healthy as before. Nevertheless, diffuse hair loss can be treated well. Read more about the symptoms, progression and treatment options here.