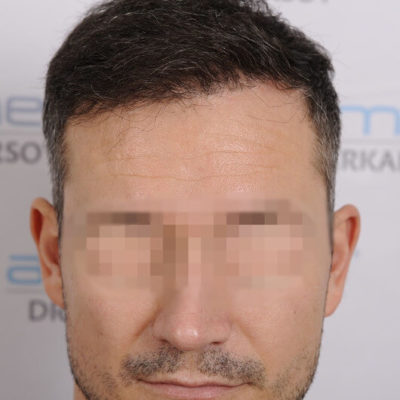
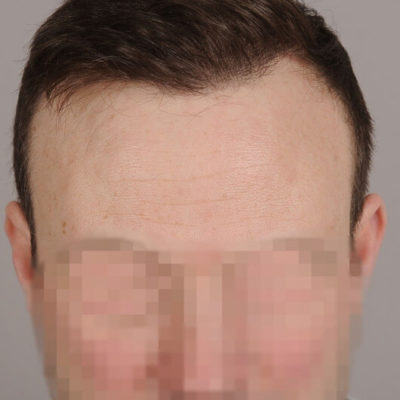
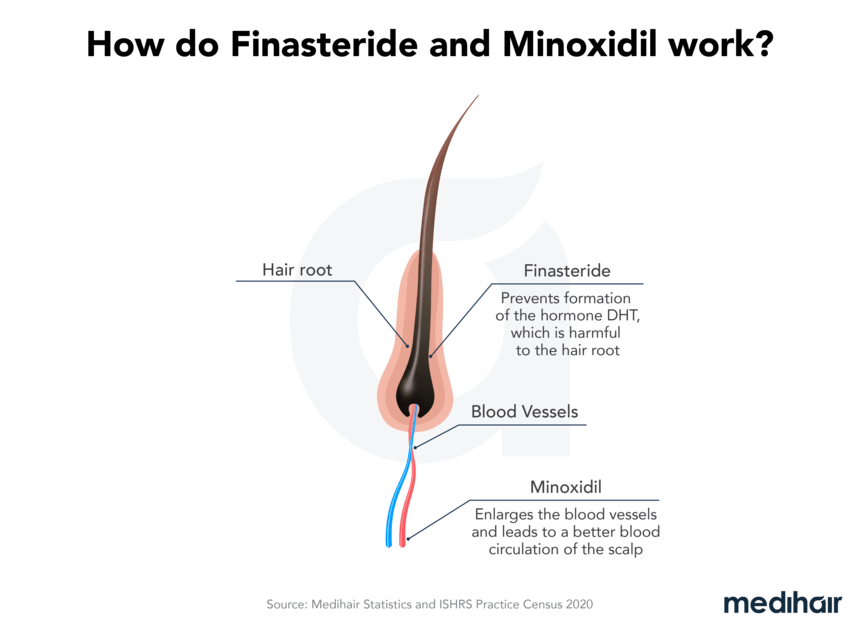
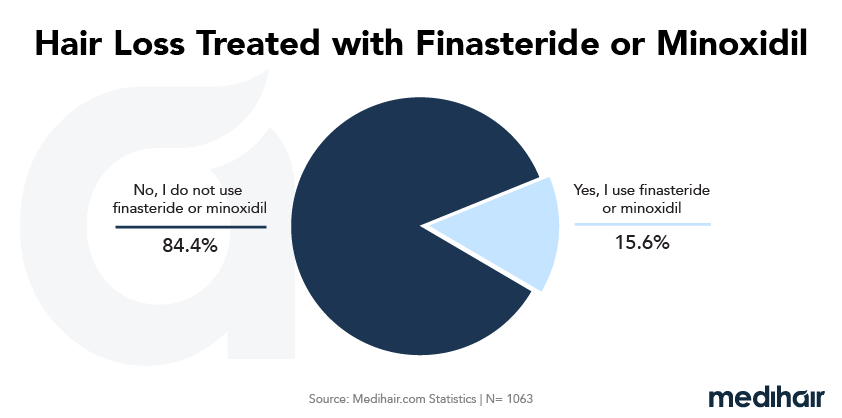What is topical finasteride?

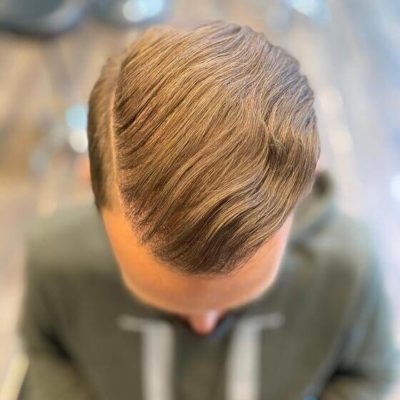
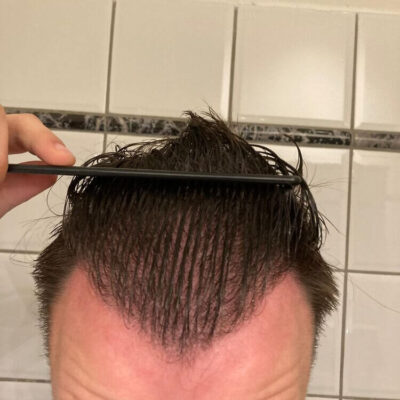
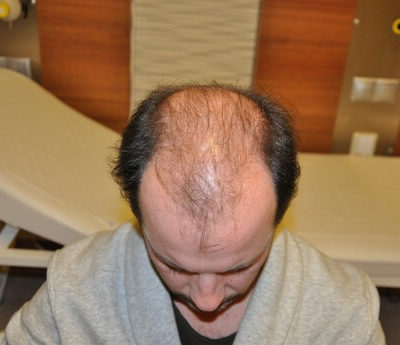
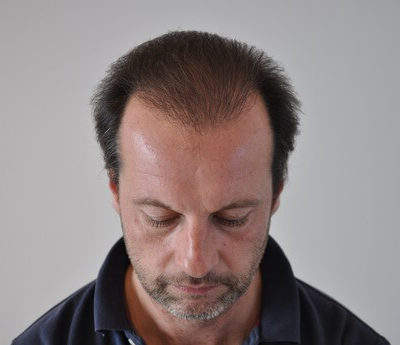
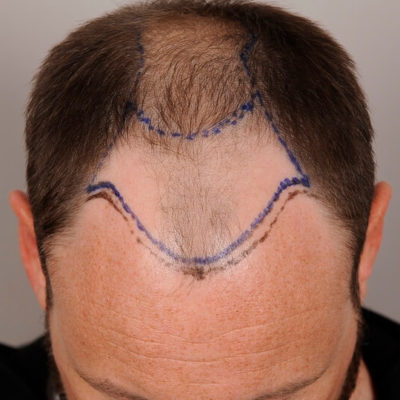
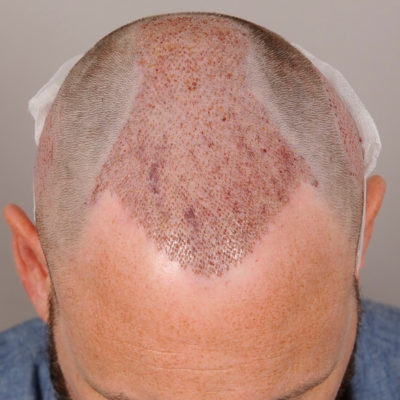
Androgenetic alopecia otherwise known as male pattern baldness is a widespread problem many people face at some point in their life. Thus, it has been a prolific topic for discussion in the medical and beauty field. Hair loss problems can be treated differently, and the key factor is to choose a suitable treatment for the particular case. The treatment may range from over-the-counter pills to different procedures and even hair transplants.
In a Nutshell
| Types | Topical or Oral Finasteride |
| Use | Scalp area |
| Side effects | Sexual dysfunction, decreased libido etc. |
| Alternatives | Minoxidil, dutasteride, hair transplant etc. |
| Pro | Cons |
|---|---|
| Tablet finasteride has been approved by FDA for treating hair loss. | The topical finasteride has not been approved by FDA for treating hair loss. |
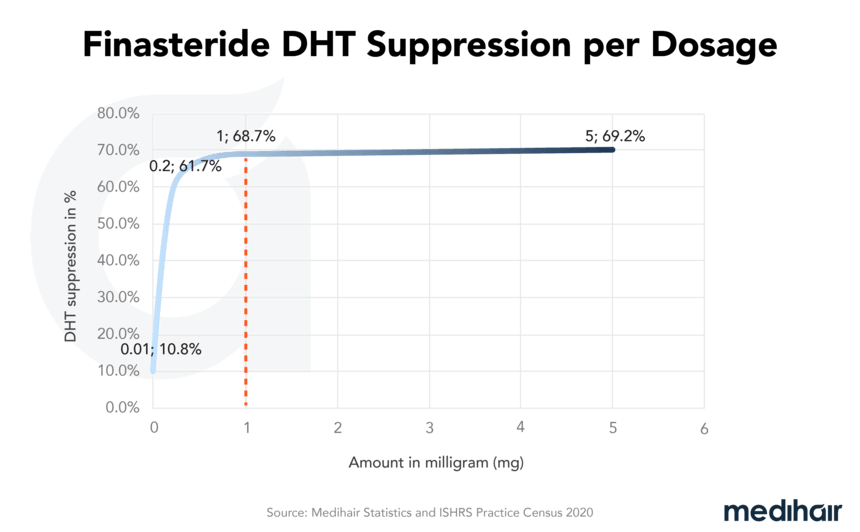
| Dihydrotestosteron (DHT) levels were decreased by 64% when using a 1 mg dose, according to the Drake studies. | Some possible side effects are erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, depression, swelling, dizziness, etc. However, according to Drake studies, decreased libido was spotted in 2.6% of cases when using 1 mg finasteride. In comparison, the placebo group showed 4.5%. |
| 48% of men have experienced improved hair growth compared to 7% of the placebo group after one year, according to Kaufman’s studies. | The topical form of the finasteride may cause skin irritation, while the tablet form may cause more potent side effects (according to some studies). |
| Roberts’ studies show that finasteride helps improve hair growth and hair count. | Topical finasteride cannot be obtained commercially yet, only by the doctor’s prescription in compound pharmacies. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How dangerous is topical finasteride?
What happens if I stop applying topical finasteride?
How long does it take for topical finasteride to take effect?
Sources