Alopecia Areata: Causes, Treatments, Costs

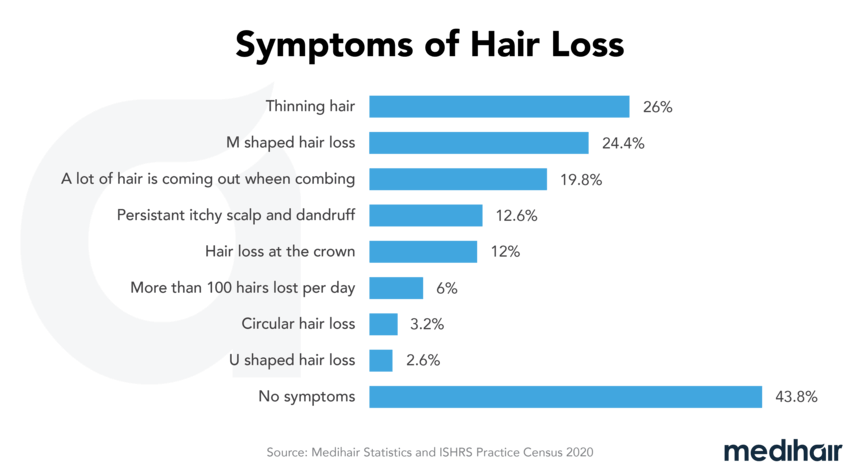
Alopecia Areata refers to a form of inflammatory hair loss. The causes are largely unknown, although many people are affected by this particular form of hair loss. With alopecia areata, the hair falls out in a circular shape and the areas continue to spread from the center of the bald patch. As a rule, not a single hair remains in the bald patches. Find out all about the causes, effective treatments and what you should avoid in this guide.
Most Important Findings
| Diagnosis | Incorrect reaction of the immune system |
| Treatments | Topical immunotherapy etc. |
| Costs | 500 - 1,000 EUR |
- Free
- Fast
- Non-binding
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alopecia Areata?
What is the cause of Alopecia Areata?
How is Alopecia Areata treated?
Sources